Integrated Rate Law for Zero and First Order Reactions
Integrated Rate Law for Zero and First Order Reactions: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Zero Order Reactions, Integrated Rate Equation for Zero Order Reactions, Time-Concentration Graph for Zero Order Reactions, First Order Reactions, and Integrated Rate Equation for First Order Reactions.
Important Questions on Integrated Rate Law for Zero and First Order Reactions
A first order reaction is complete in minute. Calculate the time taken for the reaction to be complete:
,
In a first-order reaction, the concentration of reactant decreases from in. The rate constant of reaction in is
For a zero-order reaction, with the initial reactant concentration , the time for completion of the reaction is:
Which of the following is incorrect?
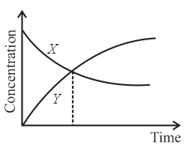
The accompanying figure depicts the change in concentration of species and for the elementary reaction as a function of time. The point of intersection of two curves represents:
The order of a reaction for which a linear line (with a negative slope) is obtained in a graph of vs is:
Two-third life for a first-order reaction is minutes. The value of its velocity constant is nearly
Consider a reaction that is first order in both directions
Initially only is present, and its concentration is Assume and are the concentrations of at time and at equilibrium, respectively. The time at which is:
For a first order reaction , the rate constant is . If the initial concentration of is , the concentration of at any time is given by the expression:
The time taken for the completion of three-fourths of a first-order reaction is
The half-life period for a zero order reaction is equal to:
Show that, In a first order reaction, time required for completion of is _____ times of half life. ().
The half-life period of a zero order reaction product is given by:
A first order reaction has reaction constant, . The half-life of the reaction in seconds is: _____
The plot of concentration of a reactant vs time for a chemical reaction is shown below.
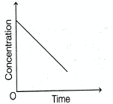
The order of this reaction with respect to the reactant is
A reaction occurs by the following mechanism:
(i)
(ii)
The net reaction is:
The half life of first order reaction is hours. Time take (in hours) for the concentration of reactant to decrease from to is:
A first order reaction takes minutes for decomposition. Calculate half life?
Rate constant of a chemical reaction is . Calculate the order of reaction?
What is the mathematical relation between half life of zero order reaction and its rate constant.
